Abstract
Background. Waldenström's macroglobulinemia (WM) is characterized by a lymphoplasmacytic infiltration of the bone marrow (BM) along with a serum monoclonal IgM and includes MYD88 L265P and CXCR4 mutations in around 90% and 25% respectively (Treon, NEJM 2012; Hunter, Blood 2014). CXCR4WHIMmutations confer worse outcome and are associated with larger BM involvement and less adenopathies (Treon, Blood 2014). One hallmark and histological criteria for WM diagnosis is the presence of numerous mast cells (MC) segregating with tumor cells in the BM (Waldenström, Acta Haematologica 1958). MC have been shown to support lymphoplasmacytic cell growth, through CD154/CD40 signaling (Tournilhac, Ann Oncol 2006), but there is so far no clear demonstration of the prognostic impact of BM MC density in WM.
Aim. We proposed to investigate BM MC density by using sensitive and specific digital quantification, allowing the analysis of large tumor cell infiltrated BM area, in order to assess its clinical relevance in WM.
Methods. A total of 65 WM patients were investigated, including 54 pts at diagnosis and 11 at relapse. Mutational status could be determined in 35 pts: allele specific PCR found MYD88 L265P mutation in 32/35 pts (91%) and deep next-generation analysis found CXCR4WHIMmutation in 7/35 (20%) pts. Diagnostic and treatment criteria for WM fulfilled recommendations of the 8th international WM workshop (Castillo, BJH 2016 ; Leblond, Blood 2016). MC density was explored using a digital tool previously used for quantifying immune cells infiltrates on tumor tissues sections (Galon, Science 2006). Tryptase and CD20 immunohistochemisty stainings were done on contiguous sections of deparaffinized BM trephine biopsies. After numerization of each section, BM surface area was manually marked out, excluding bone framework and adipocytes, in order to limit subsequent analyses to hematopoietic tissue. We then defined optimal thresholds for horseradish peroxidase signal detection. MC were counted up with "Immunoscore module" (Definiens Developer XT), on the hematopoietic tissue of the whole BM section : MC density was automately recorded as the number of tryptase positive cells per unit of selected bone marrow tissue surface area.
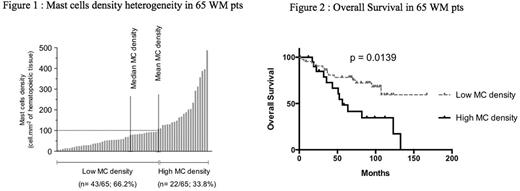
Results. MC density was found to be heterogeneous over BM, with a mean of 106 MC.mm-2 of hematopoietic tissue (Figure 1). Higher MC density (> 100 MC.mm-2) was associated with larger BM involvement by WM cells (BM deep infiltration (p=0.039) and diffuse tumor pattern (p=0.003)) and with less frequent spleen involvement (p=0.011) and a trend towards less lymph node (p=0.072) and liver (p=0.054) involvement. Higher MC density was also associated with features of advanced disease such as anemia (<115g.L-1 ; p = 0.041), thrombocytopenia (<100G.L-1 ; p=0.01) and lower albumin rate (<35g.L-1 ; p=0.03)). Furthermore MC density was 194 MC.mm-2 in patients with high IPSS, 82.4 MC.mm-2 in those with intermediate IPSS and 67.9 MC.mm-2 in those with low IPSS (p=0.0003). Regarding outcome, patients with higher MC density had a shorter median OS (56.5 months vs non reached in patients with low MC density, p = 0.0139)) (Figure 2). Among the pts scheduled to receive a 1st line treatment for an active disase (n=43) and molecularly characterized (n=20), those with CXCR4WHIM mutations had a significantly higher MC density (240.7 MC.mm-2vs 90.9 MC.mm-2 for CXCR4 WT pts ; p=0.0221).
Conclusion. By using specific digital tool on well-outlined hematopoietic tissue surface, MC density can be accurately measured in WM patients. High MC density is associated with aggressive features, poor clinical outcome and possibly with CXCR4WHIM mutation.
Ysebaert: Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Leblond: Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Servier: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Hermine: Hybrigenics: Research Funding; INatherys: Equity Ownership, Research Funding; AB Science: Equity Ownership, Honoraria, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding. Guieze: GILEAD: Other: Educational Presentation; ABBVIE: Other: Educational Presentation; JANSSEN: Other: Educational Presentation. Tournilhac: Janssen: Honoraria, Other: travel funding; AMGEN: Other: Travel funding, Research Funding; ROCHE: Honoraria, Other: Travel funding, Research Funding; GILEAD: Honoraria, Other: Travel Funding, Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria, Other: Travel funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal